What to Understand about the Threats of Radon Gas in Your Home
What are the signs of radon poisoning?
There are no safe radon levels. Any exposure to the gas, no matter how small, can cause damage to the DNA in your lung, the lower the levels found in your home, the lower the risk you have of developing lung cancer.
For most individuals, the biggest potential resource of radon direct exposure remains in their house. You can examine radon levels in your home to establish if you need to take actions to lower them.
According to the EPA, the ordinary indoor radon level is about 1.3 picocuries per liter (pCi/L). Individuals ought to take action to reduced radon degrees in the home if the level is 4.0 pCi/L or greater. The EPA estimates that virtually 1 out of every 15 houses in the USA has elevated radon degrees. Percentages of radon can additionally be launched from the water system into the air.
There are multiple choices for screening for radon in your house. Acitvated charcoal kits are an easy, in the house, choice to examine for radon. Other tests intend to detect the alpha particles emmitted by radon. There are two typical air flow options to remediate high levels of radon.
How bad is a radon level of 8?
The EPA strongly recommends radon mitigation if your radon levels are above 4 pCi/L. While radon levels below 4 still pose a health risk. They recommend you consider mitigation if your radon levels are between 2 and 4 pCi/L. They are quick to point out radon mitigation that there is no known safe level of radon.
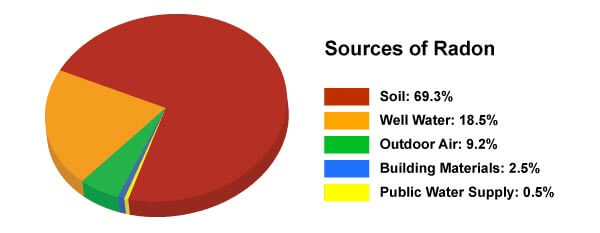
Water that originates from deep, below ground wells in rock may have higher levels of radon, whereas surface water (from lakes or rivers) generally has very reduced radon levels. For the most part, water does not add much to general direct exposure to radon. It is usually found at extremely reduced degrees in outside air and also in alcohol consumption water from rivers and lakes. It can be found at higher levels airborne in residences as well as various other structures, as well as in water from underground resources, such as well water. The dust is caught in our respiratory tracts and also releases radiation that harms the inside of our lungs.
Radon in Dirt.
Why is radon bad for you?
Radon produces a radioactive dust in the air we breathe. The dust is trapped in our airways and emits radiation that damages the inside of our lungs. This damage, like the damage caused by smoking, increases our risk of lung cancer.
Radon tests determine radon levels in picocuries per litre of air. While there is no risk-free level of radon, the Epa established an action level of 4 picocuries per liter, or pCi/L. This suggests that when radon degrees reach or go beyond 4 pCi/L, you have to take action to repair the trouble. Long-term radon testing works similarly as temporary; however, it evaluates the location for 90 days instead of an optimum of 7. It's clearly the extra time-consuming option, but it's likewise the much more accurate one.
These dose price quotes are important components of lung cancer cells. Human immunodeficiency infection (HIV) infection increases the danger of lung cancer cells; this organization has come to be more vital as advancements in antiretroviral treatment decrease death from contagious causes in this populace. Lastly, in creating countries, chronic exposure to wood smoke is thought to be responsible for a substantial fraction of lung cancers cells, particularly among ladies.
Across the country, the EPA approximates that regarding 21,000 people die every year from radon-related lung cancer cells. As many as 1 in 15 UNITED STATE residences have high degrees of radon, according to the EPA. But particular geographical regions are more likely to be impacted.

What do you do if your house has radon?
Radon can seep into any home that is in contact with the ground. It is undetectable unless you perform a radon test. It is the second leading cause of lung cancer and according to the EPA and CDC, it kills more than 20,000 annually. It is not something you want in the home you are buying.
Radon gas levels that exceed the average limit are easy and cost-effective troubles to solve contrasted to the majority of residence enhancement tasks, yet taking the action to evaluate your house. or constructing for radon is very important. According to Pennsylvania's Radon Qualification Act, just the property owner, the residential property occupier or a DEP licensed radon tester has the authority to evaluate for radon gas. Mounting air flow for your cellar can also decrease the amount of radon that has the ability to collect in your home.
This suction is what draws the radon out of the soil and also right into your home. You could believe caulking the splits and the openings in the basement flooring will certainly quit the radon from going into your home. It is not likely that caulking the easily accessible splits and also joints will completely seal the openings radon needs to go into your house. The good news is, there are various other exceptionally effective ways of maintaining radon out of your residence.
Can I install my own radon mitigation system?
In most cases, pros charge about $1,500 to install a radon mitigation system, but you can do it yourself for only about $500 in materials. So if you're fairly handy and have some carpentry, plumbing and electrical skills, you can install your own system in a weekend and save yourself a thousand bucks!
- If you have concerns about radon in your residence, you can obtain aid from the EPA by calling RADON ().
- As a matter of fact, research study shows that smokers are practically 7 times most likely to establish lung cancer than nonsmokers when subjected to the exact same quantity of radon.
- However, these are generally not major contributors to the radon levels in a residence.
- Radon can enter your residence with fractures as well as holes in the foundation, through well water, and also using structure materials, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says.
Generally, the Northeast, southern Appalachia, the Midwest, and the northern levels have a tendency to have levels over the suggested limit of 4 pCi/L, while seaside areas often tend to have lower degrees. More recent homes may also have higher degrees of radon because the soil around your house is more porous, which can make it easier for radon gas to stream in. It's estimated that 1 in 15 American homes have a raised degree of radon gas.
Is a radon level of 2 safe?
Radon levels are measured in picocuries per liter, or pCi/L. Levels of 4 pCi/L or higher are considered hazardous. Radon levels less than 4 pCi/L still pose a risk and in many cases can be reduced, although it is difficult to reduce levels below 2 pCi/L. Once installed, a follow-up radon test is done.
How much does it cost to run a radon fan?
Known risk factors for lung cancer include: Risk by age: About two out of three lung cancers are diagnosed in people over age 65, and most people are older than 45. The average age at diagnosis is 71. Family history: Genetics may predispose certain people to lung cancer.
How often should you test for radon?
Living pattern changes Whenever there is a change in your home, you should perform local radon testing. It's also recommended that you test your home for radon at least twice a year too. If your tests come back unusually high, then you should order one or two more tests so that you can compare the results.
How do I know if my house has radon?
In fact, you're probably breathing it in every day, even if it's at a low level. However, you can't tell if you're breathing it in at a high level. The danger in radon exposure is that you can't see it, taste it, or smell it. And you won't have any symptoms to alert you.
Is radon only in the basement?
Radon is completely odorless as well as being invisible. Because it is often found unexpectedly in basements, some people mistakenly believe that it only occurs in basements. Most commonly homes with basements are suspect for having higher radon levels.
Is radon heavier than air?
Radon gas is approximately 7.5 times heavier than air. It is however a noble gas with no chemical More help affinity but is easily influenced by air movements and pressure. In a house with forced air heating and cooling, radon gas can easily be distributed throughout the entire dwelling.
How do I make my house safe from radon?
Install a layer of gas-permeable aggregate, such as four inches of gravel, beneath the slab or flooring system of your home if you don't have a crawlspace. Cover this layer or your crawlspace floor with plastic sheeting to stop radon gas from moving past that level and into your home.
How do you eliminate radon?
If a person has been exposed to radon, 75 percent of the radon progeny in lungs will become "harmless" lead particles after 44 years. When an alpha particle damages a cell to make it cancerous, the onset of lung cancer takes a minimum of 5 years but most often 15 to 25 years, and even longer.
How effective is radon remediation?
The Surgeon General and the EPA recommend testing for radon and reducing radon in homes that have high levels. Fix your home if your radon level is confirmed to be 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) or higher. Radon reduction systems work. Some radon reduction systems can reduce radon levels in your home by up to 99%.
What kind of cancer is caused by radon?
Radon decays quickly, giving off tiny radioactive particles. When inhaled, these radioactive particles can damage the cells that line the lung. Long-term exposure to radon can lead to lung cancer, the only cancer proven to be associated with inhaling radon.
Should I buy a house with high radon?
EPA RECOMMENDS: If you are buying or selling a home, have it tested for radon. For a new home, ask if radon-resistant construction features were used and if the home has been tested. Fix the home if the radon level is 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) or higher.
What is involved in radon mitigation?
Mitigation of radon in the air is accomplished through ventilation, either collected below a concrete floor slab or a membrane on the ground, or by increasing the air changes per hour in the building. Treatment systems using aeration or activated charcoal are available to remove radon from domestic water supplies.
Do all homes have http://daltonwmac823.raidersfanteamshop.com/examine-this-report-on-radon-systems some level of radon?
The EPA estimates the lifetime risk of radon-induced lung cancer for never-smokers at 7 per 1,000 people, compared with 62 per 1,000 for smokers exposed to a level of 4 pCi/L. Your risk goes up with your exposure to radon and cigarette smoke over time.
